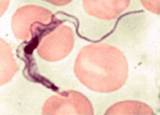
African trypanosomes are extracellular organisms, both in the mammalian and insect
host. Infection in the human host begins when the infective stage, known as the metacyclic
blood-stage trypomastigotes (long, slender forms), and divide by binary fission in the
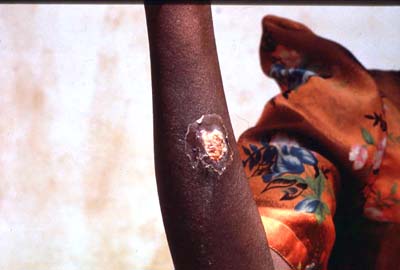
interstitial spaces at the site of the bite wound. The buildup of metabolic wastes and cell
debris leads to the formation of a chancre.
No comments:
Post a Comment